Building a High-performance Deduplication System
| Venue | Category |
|---|---|
| ATC'11 | Deduplication System |
Building a High-performance Deduplication System1. SummaryMotivation of this paperSystem DesignImplementation and Evaluation2. Strength (Contributions of the paper)3. Weakness (Limitations of the paper)4. Some Insights (Future work)
1. Summary
Motivation of this paper
Effectiveness of a deduplication system
- Deduplication efficiency how well the system can detect and share duplicate data units? (reduce the storage cost)
- Scalability the ability to support large amounts of raw storage with consistent performance (reducing the total number of nodes)
- Throughput the rate at which data can be transferred in and out the system (minimizing the length of a backup window)
It is hard to achieve all those three goals.
- The reference management problem the cost of reference management (upon addition and deletion of data) has become one of the biggest real-world bottlenecks.
take many hours per day.
- The indexing problem Need to scale to high capacities, good indexing throughput, provide high duplicate detection rate.
This paper presents a complete, single-node deduplication system that covers indexing, reference management, and end-to-end throughput optimization.
System Design
- System architecture
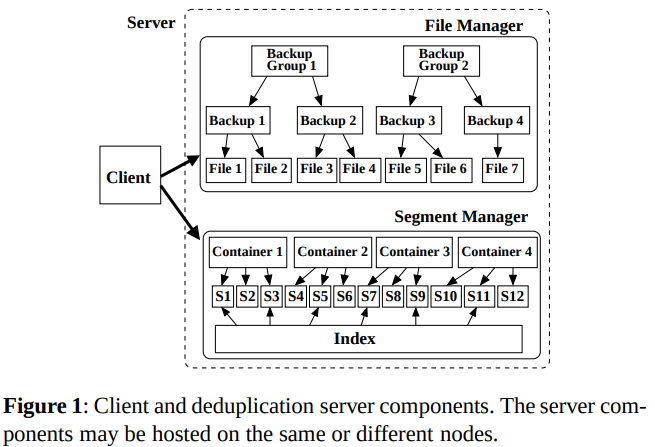
- Container: raw data + a catalog which lists all FPs stored in the container
- Three-level hierarchy in File Manager (FM): files -> backup -> backup group
allowing the FM to perform coarse-granularity tracking of file/backup changes in the system.
- Progressive Sampled Indexing Maintain a complete index is a difficult task since the index typically needs to be stored both in memory, for performance, and on disk, for durability.
- directly locatable objects: file chunk location information is stored with the file metadata, therefore removing the need to consult the index for the exact location of the file chunks.
file metadata size may increase
- sampled indexing It no longer need to maintain a full index. It can maintain a sampled indexing.
can determine the number of entries that need to be dropped.
When a lookup operation hits on a sampled FP, it can locate the container it belongs to and pre-fetch all FPs from that container's metadata into a memory cache.
- progressive sampling using the progressive sampling based on the amount of storage used, as opposed to the maximum raw storage.
- Grouped mark-and-sweep Original mark-and-sweep has poor scalability
because it needs to touch every file in the system.
Key idea of grouped mark-and-sweep: avoid touching every file in the mark phase and every container in the sweep phase.
just detect the changed backup group instead of each file. the file manager tracks the changes in each backup group only containers used by groups that have deleted files need to be swept.
- Client-server interaction Using full pipeline to achieve high throughput
can observe the length of message queue to adjust the number of worker threads.
Implementation and Evaluation
- Evaluation
- dataset
synthetic data set: consists of multiple 3GB file, each with globally unique data chunks.
stress the disk and the network systems as large amounts of data need to be transferred. VM dataset
- throughput
backup throughput: index throughput, ssd indexing throughput, and end-to-end throughput, reference update throughput, restore
- deduplication efficiency
2. Strength (Contributions of the paper)
- This paper shows the detail of implementing a index and cache index in the deduplication system.
- It also proposes progressive sampled indexing, grouped mark-and-sweep, and client-server interaction.
- this paper takes care of the issue that the how to improve the scalability issue in single-node deduplication system.
- Most other systems have provided good solutions for a subset of problems (three problems), usually excluding single-node scalability and reference management.
3. Weakness (Limitations of the paper)
- In its grouped mark-and-sweep scheme, all the containers used by groups that have deleted files need to be swept, however some containers of them maybe unchanged.
incur the high overhead in the sweep phase.
4. Some Insights (Future work)
- this paper mentions the power outages and data corruption are really not that rare in real deduplication system
need to consider the how to recover the deduplication metadata and data.
- In the restore operation, it mentions that using directly locatable objects allows it to perform restore without using the index, making the whole process very scalable.