The Hadoop Distributed File System
@MSST'10 @Introduction
The Hadoop Distributed File SystemSummaryHDFSArchitectureHDFS ClientFile I/O Operations and Replica ManagementData PipelineBlock PlacementPractice at YahooFuthre Work
Summary
Motivation of this paper:
This paper describes the architecture of HDFS and reports on experience of using HDFS to manage 25 petabytes of enterprise data at Yahpp.`
HDFS
- HDFS stores file system metadata and application data separately.
- NameNode: store metadata on a dedicated server
- DataNode: store application data on other servers
All servers are fully connected and communicate with each other using TCP-based protocols.
Architecture
- NameNode The HDFS namespace is a hierarchy of files and directories.
Files and directories are represented on the NameNode by inodes (e.g., permissions, modification and access times, namespace and disk quotas)
The NameNode maintains the namespace tree and the mapping of file blocks to DataNode. A HDFS client firstly contacts the NameNode for locations of data blocks comprising the file and then reads block contents from the DataNode closest to the client.
- DataNodes Each block replica on a DataNode is represented by two files in the local host's native file system.
- the data itself
- block's metadata including the checksums for the block data and the block's generation stamp
During the startup, each DataNode connects to the NameNode and preforms a handshake.
Purpose: verify the namespace ID and the software version
If either does not match that of the NameNode the DataNode automatically shuts down. After the handshake, DataNode registers with the NameNode.
storage ID is assigned to the DataNode when it registers with the NameNode for the first time and never chanegs after that.
- Block Report DataNode sends to NameNode the block reports including the block id, the generation stamp, and the length for each block replica the server hosts.
- Heartbeat From the a DataNode, it also carries information about total storage capacity, fraction of storage in use, and the number of data transfers currently in progress.
NameNode uses replies to heartbeats to send instructions to the DataNodes.
HDFS Client
HDFS client is a code library that exports the HDFS file system interface. (e.g., read, write, delete files, and operations to create and delete directories)
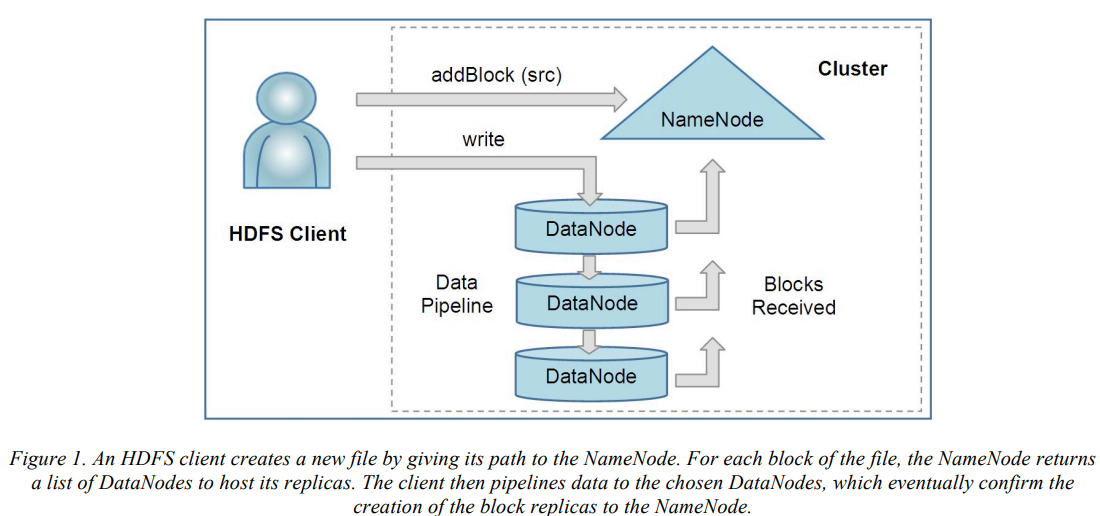
When a client opens a file to read to , it fetches the list of blocks and the locations of each block replica from the NameNode.
File I/O Operations and Replica Management
HDFS implements a single-writer, multiple-reader model.
The HDFS client that opens a file for writing is granted a lease for the file, no other client can write to file.
Data Pipeline
The DataNodes form a pipeline, the order of which minimizes the total network distance from the client to the last DataNode.
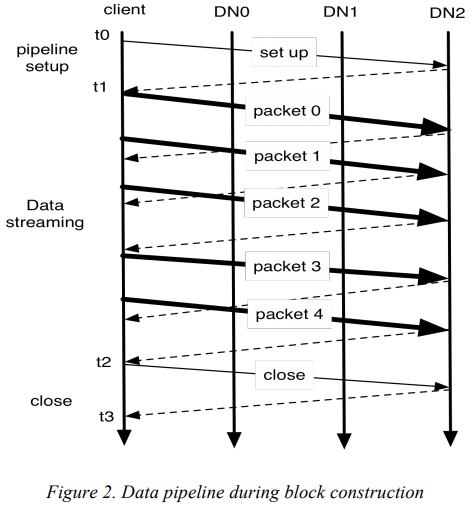 Bold lines represent data packets, dashed lines represent acknowledge messages, thin lines represent control mesages to setup and close the pipeline.
Bold lines represent data packets, dashed lines represent acknowledge messages, thin lines represent control mesages to setup and close the pipeline.
Block Placement
When a DataNode registers with the NameNode, the NameNode runs a configured script to decide which rack the node belongs to.
- The default HDFS block placement policy provides a tradeoff between minimizing the write cost, and maximizing data reliability, availability, and aggregate read bandwidth
- places the first replica on the node where the writer is located
- places the second and third replicas on two different racks.
This policy reduces the inter-rack and inter-node write traffic and generally improves write performance.
Practice at Yahoo
In this part, this paper demonstrates the configuration and data in Yahoo.
For benchmark, it uses DFSIO benchmark to measure average throughput for read, write and append operations.
DFSIO is an application available as part of the Hadoop distribution. It is designed to measure performance only during data transfer, and excludes the overheads of task scheduling startup, and the reduce task.
The NNThroughput benchmark:
it is a single node process which starts the NameNode application and runs a series of client threads on the same node.
Futhre Work
- Single Failure: The Hadoop cluster is effectively unavailable when its NameNode is down. It has taken steps towards automated failover.
Using BackupNode
- Scalability of the NameNode: it has been a key struggle. The main challenge with the NameNode has been that when its memory usage is close to the maximum tha NameNode becomes unrespomsive due to Java garbage collection and sometimes requires a restart.
their near-term solution to scalability is to allow multiple namespaces (and NameNodes) to share the physical storage within a cluster. the main drawback of multiple independent namespaces is the cost of managing them, especially, if the number of the namespaces is large.