Using Hints to Improve Inline Block-Layer Deduplication
| Venue | Category |
|---|---|
| FAST'16 | Deduplication |
Using Hints to Improve Inline Block-Layer Deduplication1. SummaryMotivation of this paperBlock-layer deduplication hintsImplementation and Evaluation2. Strength (Contributions of the paper)3. Weakness (Limitations of the paper)4. Future Works
1. Summary
Motivation of this paper
Important information about data context (e.g. data vs. metadata writes) is lost at the block layer.
This paper argues passing such context to the block layer can help improve the deduplication performance and reliability. The root cause: the semantic divide between the block layer and file systems
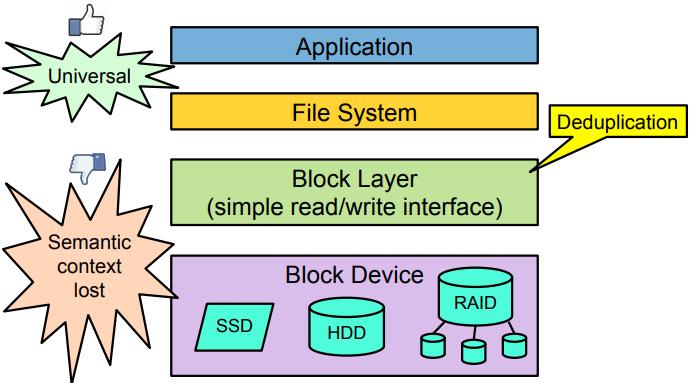
This paper proposes to design the interface in block-layer deduplication system, which can allow upper storage layers to pass hints based on the available context.
Most of existing deduplication solutions are built into file systems because they have enough information to deduplicate efficiently without jeopardizing reliability. This information can be leveraged to avoid deduplicating certain blocks (e.g., metadata)
Block-layer deduplication hints
- Hints Hinting asks higher layers to provide small amounts to extra information to the deduplication. In this paper, it uses hinting to recover context at the block layer.
- Two main advantages in block-layer deduplication
- allowing nay file system and application to benefit from deduplication
- ease of implementation
- Potential Hints
- Bypass deduplication (NODEDUP) Main idea: some writes are known a priori to be likely to be unique. Attempting to deduplicate unique writes wastes CPU time on hash computation and I/O bandwidth on maintaining the hash index.
application requirement: generate data should not be duplicated. (random data or encrypted data) Overhead: hash computation, index size, more RAM space, more lookup bandwidth. main issue: unique data and reliability
For metadata: Most file system metadata is unique
metadata writes are more important to overall system performance than data writes becasue the former are oftern synchronous. add deduplication to metadata might increase the latency of those critical metadata writes. reliability: duplicates metadata to avoid corruption.
- Prefetch hashes (PREFETCH) When a block layer deduplication knows what data is about to be written, it can prefetch the corresponding hashes from the index
accelerating future data writes by reducing lookup delays. inform the deduplication system of I/O operations that are likely to generate further duplicates (copy file) their hashes can be prefetched and cached to minimize random accesses.
- Other Bypass compression, cluster hashes, partitioned hash index, intelligent chunking
cluster hashes: files that reside in the same directory tend to be accessed together.
Implementation and Evaluation
- Implementation
Modify the write path and read path.
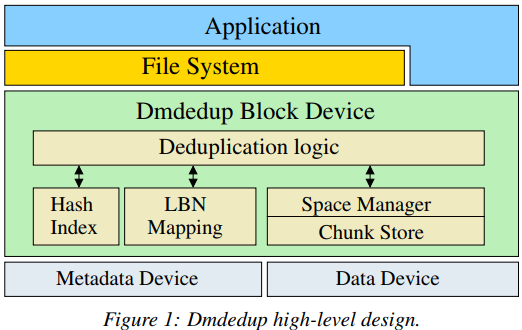
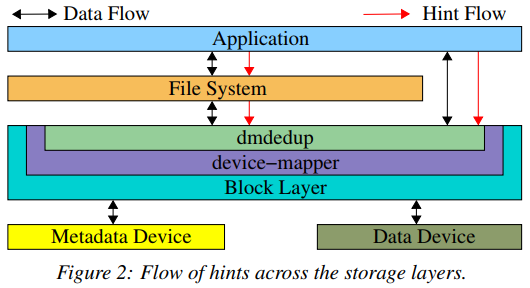
- Evaluation
- NODEDUP: observe the elapsed time in four file systems
no-hint v.s. hint-on
- PREFETHCH: observe the elapsed time in four file systems
no-hint v.s. hint-on
- Throughput: using Filebench
2. Strength (Contributions of the paper)
- This paper states that if a block-level deduplication system can know when it is unwise to deduplicate a write, it can optimize its performance and reliability.
- This method can be useful when writing unique data (i.e., avoid wastage of resources) or need to store duplicate chunks for reliability.
3. Weakness (Limitations of the paper)
- In my opinion, the idea in this paper is just to deliever the context information to the block-layer to let block-layer deduplication do better.
4. Future Works
- This work mentions that its initial experiments result is successful, and it can add more hints to provide more information in block-layer
provide richer context to the block layer.