Message-Locked Encryption and Secure Deduplication
| Venue | Category |
|---|---|
| EuroCrypto'13 | Secure Deduplication |
Message-Locked Encryption and Secure Deduplication1. SummaryMotivation of this paperMLE definitionsImplementation and Evaluation2. Strength (Contributions of the paper)3. Weakness (Limitations of the paper)4. Some Insights (Future work)
1. Summary
Motivation of this paper
The formulation of MLE
- the key under which encryption and decryption are performed is itself derived from the message.
- definitions both for privacy and for a form of integrity (tag consistency).
There is an absence of a theoretical treatment for MLE in secure deduplication deployment.
- It is not clear what precisely is the underlying security goal and whether deployed schemes achieve it.
MLE definitions
General MLE syntax
- key generation algorithm: K
- encryption algorithm: E
- decryption algorithm: D
- tagging algorithm: T
For convergent encryption:
- K = H(M)
- C = E(K, M)
- T = H(C)
Privacy:
No MLE scheme can achieve semantic-security-style privacy
if the target message is drawn from a space of
- given an encryption of , it can recover in trials.
- the best possible privacy: semantic security when message are unpredictable (have high min-entropy)
Tag consistency: (how to against the duplicate faking attacks)
TC: an adversary cannot make an honest client recover an incorrect message, meaning one different from the one it uploaded. (cannot protect the message integrity)
STC: an adversary cannot erase an honest client's message.
STC is strictly stronger than TC.
If an MLE scheme is deterministic, letting the tag equal the ciphertext will result in a scheme that is STC secure.
- CR-hashing the ciphertext preserves STC, but the performance is not good.
Discussion: for upload operation
- the client stores securely (may store encrypted under its password on the server, but the implementation is not relevant here).
- the client sends the to the server.
- the server computes tag . (the main issue)
Fast MLE schemes
CE: convergent encryption
HCE1 (Hash-and-CE 1, in TahoeFS)
- compute the tags during encryption by hashing the per-message key (), and including the result in the ciphertext.
- offload the work from the server to the client and reduces th e number of passes needed to encrypt and generate a tag from three to two.
HCE2
- include the guarded decryption
- recomputing the tag using the just-decrypted message.
RCE
- randomized convergent encryption
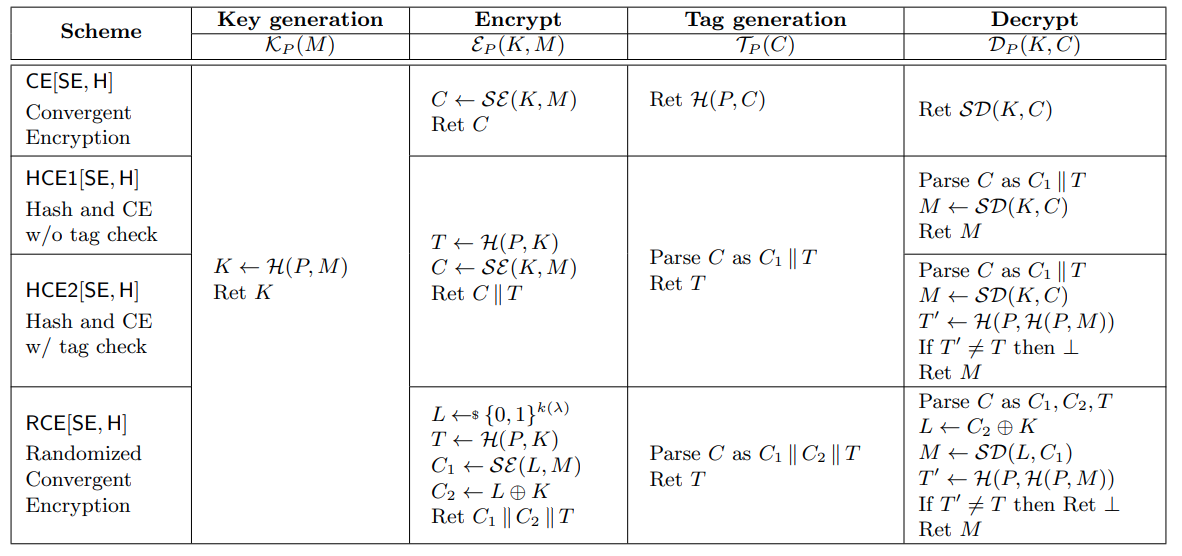
- randomized convergent encryption
Performance of each MLE scheme
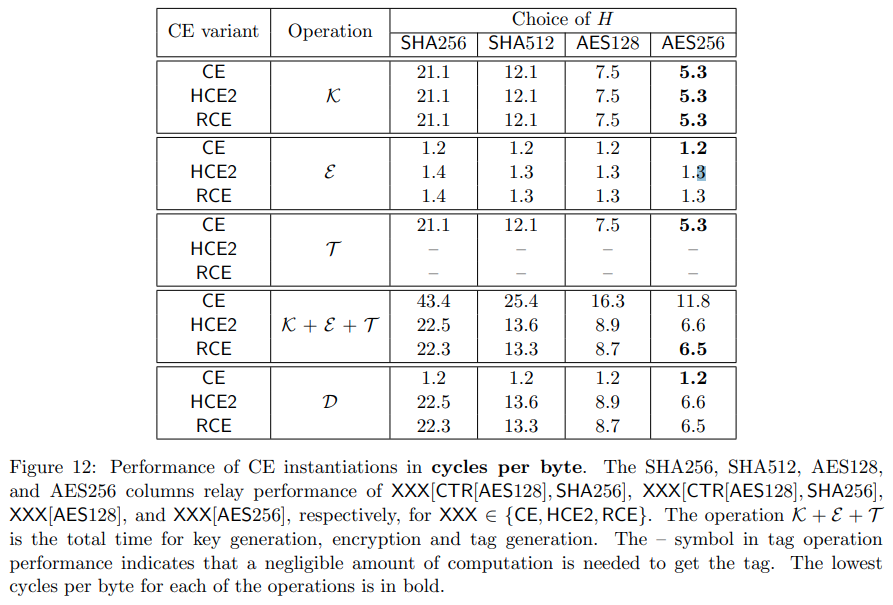
Implementation and Evaluation
2. Strength (Contributions of the paper)
- Practical contribution ROM security analyses of a natural family of MLE schemes (include deployed schemes).
- Theoretical contribution Standard model solution, the connection with deterministic encryption, hash functions.
different trade-offs between assumptions made and the message distributions for which security is proven.
- Provide four MLE schemes with different trade-offs between the security and performance.
CE, HCE1, HCE2. RCE
3. Weakness (Limitations of the paper)
4. Some Insights (Future work)
- This paper mentions the issue that how to generate the tag?
: , , : , ,
The can offer better performance for the server who can simply read the tag as the second part of the ciphertext rather than needing to compute it by hashing the possibly long ciphertext.
vulnerable to duplicate faking attacks
- the length of the key It insists that an MLE scheme have keys that are shorter than the message.
- Tag consistency theorem
- Any deterministic scheme is STC-secure when tags are CR-hashes of the ciphertext.
- If is CR-secure then HCE2 and REC are TC-secure.