Rekeying for Encrypted Deduplication Storage
| Venue | Category |
|---|---|
| DSN'16 | Secure Deduplication |
Rekeying for Encrypted Deduplication Storage1. SummaryMotivation of this paperREEDImplementation and Evaluation2. Strength (Contributions of the paper)3. Weakness (Limitations of the paper)4. Future Works
1. Summary
Motivation of this paper
Replacing an existing key with a new key for encryption
it can renews security protection, so as to protect against key compromise and enable dynamic access control in cryptogrephic storage.
This paper implements a rekeying-aware encrypted deduplication storage system.
to realize efficient rekeying trade between performance and security, achieve dynamic access control
Why realizing efficient rekeying in encrypted deduplication storage is challenging?
- if it renews the key by renewing the derivation function any newly stored message encrypted by the new key can no longer be deduplicated with the existing identical message.
- if it re-encrypts all existing messages with the new key , then there will be tremendous performance overheads.
Key Question: how to enable secure and lightweight rekeying, while preserving the deduplication capability?
REED
- Main idea: REED encrypts a small part of the package with a key that is subject to rekeying, while the remaining large part of the package is generated from a deterministic variant of AONT.
preserve content similarity. sacrificing a slight degradation of storage efficiency.
Augments CAONT to enable rekeying
- generate a CAONT package with the MLE key as an input
- encrypt a small part of the package with the file key stab
- Since the stab is very samll, the rekeying overhead can be mitigated.
- System model In this work, it still keeps a dedicated key manager server
for key generation resisting brute-force attack
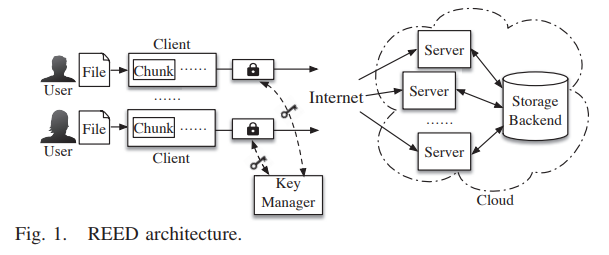
- Threat model
- An honest-but-curious adversary Aims to learn the content of the files in outsourced storage.
can compromise the cloud (any hosted server and the storage backend): all stored chunks and keys can collude with a subset of unauthorized or revoked clients can monitor the activities of the clients, identify the result returned by the key manager.
- the key manager is deployed in a fully protected zone
an adversary cannot compromise or gain access to the key manager.
- Server-side deduplication it does not introduce any side channel in deduplication.
- Two rekeying-aware encryption schemes
- Basic encryption scheme
- Modify the cryptographic hash key in CANOT by the corresponding MLE key generated by the key manager.
- append a publicly known, fixed-size canary to for CANOT, so that the integrity of can be checked.
- Enhanced encryption scheme Goal: against the adversary to compromise the MLE key, the adversary can recover the pseudo-random mask.
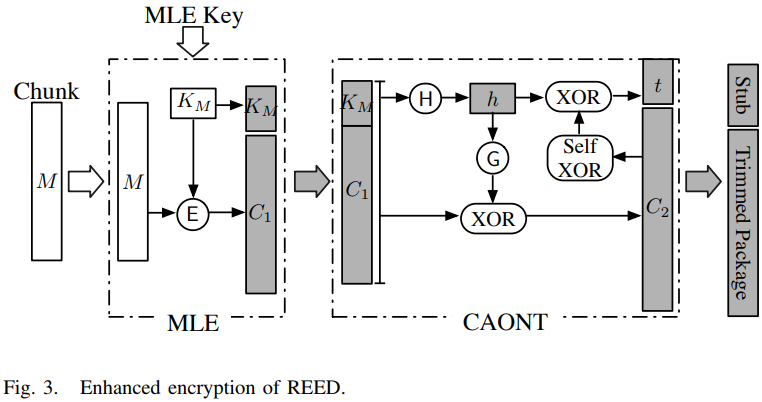
Need an additional encryption step.
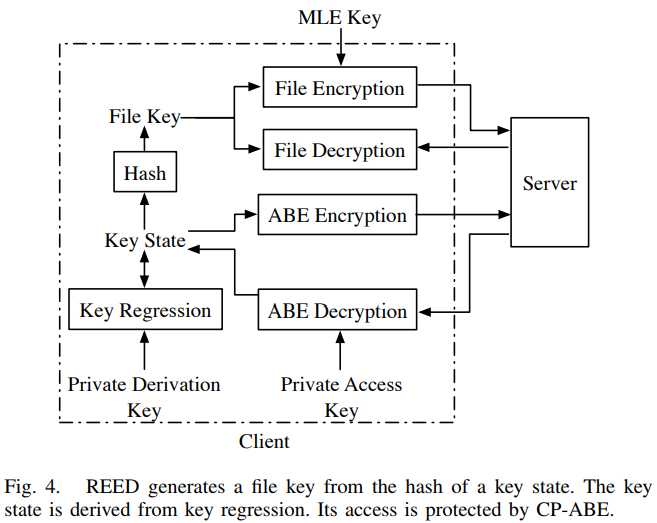
- Dynamic access control Associating each file with policy
ciphertext policy attribute-based encryption (CP-ABE): can be used to control the access privileges. key regression
Implementation and Evaluation
- Implementation C++: extend CDStore to support the rekeying Some points: batching, caching, parallelization
mitigate computational and I/O overhead
- Evaluation setting One REED client, one key manager, and five REED servers
four of the five servers manages the key store
Datasets:
Synthetic data: 2GB file of the synthetic data, load the synthetic data into memory to avoid generating any disk I/O overhead Real-world data: FSL trace: 2013
- MLE key generation performance
fix the batch size as 256 per-chunk key generation requests. Around MB/s MLE key generation performance: start from sending the blinded fingerprints to the key manager
- Encryption performance
observe that the encryption speed is not the performance bottleneck in REED (network speed Gb/s)
- Upload and download performance including the chunking, key generation, encryption, and data transfer.
the main bottleneck is the MLE key generation speed. eight clients: MB/s
2. Strength (Contributions of the paper)
- This paper proposes two encryption schemes for REED, which trades between performance and security.
the enhanced scheme is resilient against key leakage through a more expensive encryption.
3. Weakness (Limitations of the paper)
4. Future Works
- In this paper, it mentions the design of a single key manager can be generalized for multiple key managers for improved availability.
- The idea of this paper is to offload the rekeying operation to the stub, by this way it can reduce the overhead of update, and preserve the deduplication for the trimmed package.