SPEED: Accelerating Enclave Applications via Secure Deduplication
| Venue | Category |
|---|---|
| ICDCS'19 | Computation Deduplication |
SPEED: Accelerating Enclave Applications via Secure Deduplication1. SummaryMotivation of this paperSPEEDImplementation and Evaluation2. Strength (Contributions of the paper)3. Weakness (Limitations of the paper)4. Some Insights (Future work)
1. Summary
Motivation of this paper
Motivation
Existing approaches to accelerate applications in the context of Intel SGX.
- asynchronous system calls.
- exit-less remote procedure calls: mitigate the cost of enclave exit.
A new angle to optimize the performance of applications in SGX
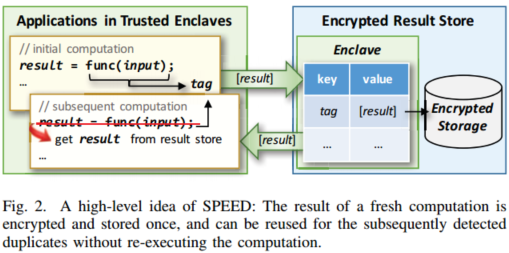
- cache or reuse the results of previous computations.
- computation deduplication in the context of SGX is till a non-trivial task.
a particular computation is deterministic yet time-consuming.
- it would be more efficient to cache and reuse the same result rather than re-computing it.
Main issues
- bind a particular computation to its result
- consider both function's code and input data
- manage reusable results efficiently and securely
- small TCB size
- store data outside the enclave
- share these encrypted results between different applications
- MLE
- without sharing a system-wide secret key among all applications, which is vulnerable to the potential single point of compromise.
SPEED
Architecture
- DedupRuntime: a secure deduplication runtime as a trusted library
- ResultStore: a generic encrypted result store
- Developers: the developer are willing to harden their applications with the recent advancement in hardware-assisted security technologies.
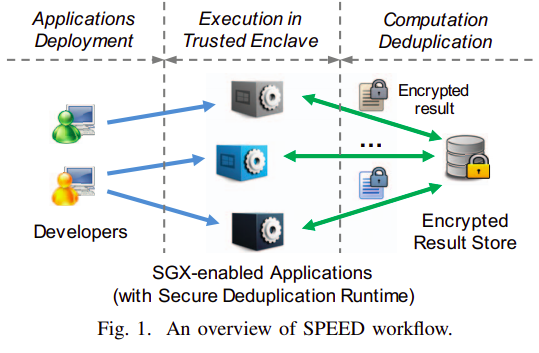
Threat model
a powerful adversary: control the software stack of physical machines, including hypervisor and OS.
TEE cannot be compromised, do not consider the side-channel attacks.
protect: the function's code, input data, and computation results.
- may leakage whether an intended computation has been done before.
Whole workflow
DedupRuntime:
- Does not require to share a system-wide secret key in advance.
- , for function

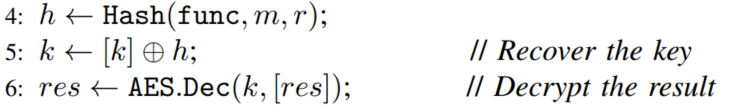
- intercepting marked function calls, querying ResultStore, and retrieving the possible computation results.
ResultStore:
- enclave-protected dictionary
- keep only small-sized metadata inside the enclaves (pointers)
- storing the actual content outside
Implementation and Evaluation
Implementation
- C++, SGX SDK
Datasets
- computer version
- data compression
Evaluation
developer effort
- only requires very little modifications as few as 2 lines
application performance
- without using SPEED
- initial computation with SPEED
- subsequent computation with using SPEED
cryptographic operations
- tag generation is the bottleneck
2. Strength (Contributions of the paper)
- propose the first secure and generic computation deduplication system SPEED.
protect and reuse computation results across multiple applications.
- implement a fully functional prototype with Intel SGX SDK.
open-source in github
3. Weakness (Limitations of the paper)
- do not test the dataset with a large size.
performance is poor with the data is large
4. Some Insights (Future work)
SGX background
Intel SGX
- it is popular in academia and industry.
AMD TrustZone
SGX research direction
how to reduce the performance overhead of the SGX
eliminate the expensive context switches in enclave application
design more efficient memory management scheme
- maintain user-level page table in enclave for exit-less paging
deduplicating the repeated and often time-consuming computation