Tradeoffs in Scalable Data Routing for Deduplication Clusters
| Venue | Category |
|---|---|
| FAST'11 | Distributed Deduplication |
Tradeoffs in Scalable Data Routing for Deduplication Clusters1. SummaryMotivation of this paperMethod Implementation and Evaluation2. Strength (Contributions of the paper)3. Weakness (Limitations of the paper)4. Future Works
1. Summary
Motivation of this paper
- Motivation To meet increasing requirements, its goal is to design a backup storage system large enough to handle multiple primary storage systems.
build a deduplication cluster storage system with individual high-throughput nodes. a cluster-wide data reduction ratio close to that of a single very large deduplication system.
- Problem
- there is a tension between deduplication effectiveness and throughput.
using superchunk.
- the risk of creating duplicates since the fingerprint index is maintained independently on each node.
routing algorithm
- the system can overload a single node by routing too much data to it.
load balancing
Method
- System Architecture
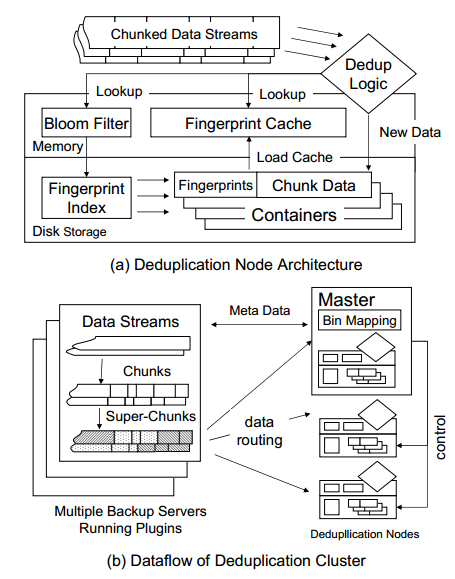 group chunks into a superchunk , and routes each superchunk to a deduplicating storage node.
group chunks into a superchunk , and routes each superchunk to a deduplicating storage node.
for high throughput.
- Load balance (rebalancing) use a level of indirection called a bin, assign a superchunk to a bin using the mod function.
map each bin to a given node.
Bin migration occurs when the storage usage of a node exceeds the average usage in the cluster by some threshold. (defaulting to 5%)
Data Routing
- stateless routing: light-weight and well suited for most balanced workloads.
- stateful routing: requiring more overhead but maintain a higher deduplication rate with larger clusters.
- Stateless routing produce a feature value representing the data and then apply a simple function to the value to make the assignment.
how to represent a superchunk? use the first, maximum, minimum, or most common fingerprint.
suppose the hash values are often uniformly distributed.
Advantages
1) reduce overhead for recording node assignments 2) reduce requirements for recovering this state after a system failure.
Disadvantages
1) potential loss of deduplication 2) potential for increased data skew if the selected features are not uniformly distributed
- Stateful routing Using information about the location of existing chunks can improve deduplication.
use Bloom filter to count the routing algorithm of times each fingerprint in super-chunk is already stored on a given node. vote-based approach, if the highest weighted vote is above a threshold, select that node.
voting benefit threshold
To mitigate the overhead of Bloom filter lookup
N chunks, M nodes, MN lookups
Sample some chunks for lookup
, reduce the Bloom filter lookup.
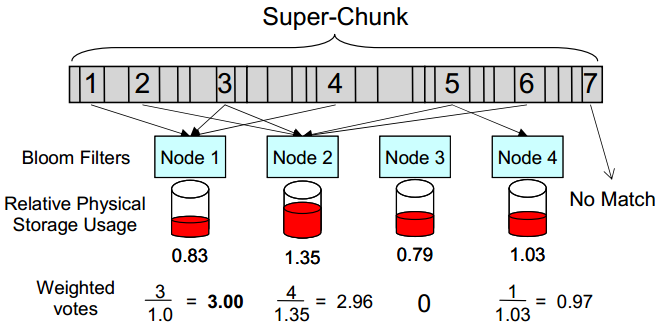
Advantages
1) provide the opportunity to incorporate expected deduplication and capacity balancing while assigning chunks to nodes.
Disadvantages
1) increased cost in computation and memory or communication overhead
Implementation and Evaluation
Evaluation
- Dataset: 9 datasets
- Superchunk size: 1MB
- trace-driven simulation
Metrics
- Total Deduplication
- Data skew
- Effective Deduplication (ED)
- Normalized ED
- Fingerprint index lookups
Feature selection
- Using 4 features: hash(64) of the first chunk, hash(*) of the first chunk, the minimum of all hash(64), the minimum of all hash(*)
2. Strength (Contributions of the paper)
- provide a deep study of the properties of both stateless and stateful versions of super-chunk routing.
- extensive experiments to show that sensitive analysis.
3. Weakness (Limitations of the paper)
4. Future Works
- Choosing the right chunk granularity presents a tradeoff between deduplication and system capacity and throughput even in a single-node system.
- 1MB superchunk size is good tradeoff between index lookups.
impact deduplication throughput, and effective cluster-wide deduplication.