UKSM: Swift Memory Deduplication via Hierarchical and Adaptive Memory Region Distilling
| Venue | Category |
|---|---|
| FAST'18 | Memory Deduplication |
UKSM: Swift Memory Deduplication via Hierarchical and Adaptive Memory Region Distilling1. SummaryMotivation of this paper:UKSMTechnology 1: Hierarchical Region DistillingTechnology 2: Adaptive Partial HashingImplementation and Evaluation2. Strength (Contributions of the paper)3. Weakness (Limitations of the paper)4. Future Works
1. Summary
Motivation of this paper:
The responsiveness of the memory deduplication process is very important to newly generated pages. If the deduplication approach cannot catch up with the generation speed of memory redundancy, memory pages would be swapped out to the disk, and the whole system is slowed down.
State-of-art Content Based Page Sharing (CBPS) approaches lack reponsiveness as they equally scan every page to find redundancies.
- Two key observations
- Most pages within the same regio present similar duplication pattern.
- Partial page hashing need to be adaptive.
UKSM
- Main idea:
- do not treat each page equally, prioritizes different memory regions (with different CPU cycles, different sample intervals) to accelerate the deduplication process.
- To identify whether two pages are same, partial page hashing needs to be adaptive to the dynamic workload (to achieve more cost-effective scanning).
Technology 1: Hierarchical Region Distilling
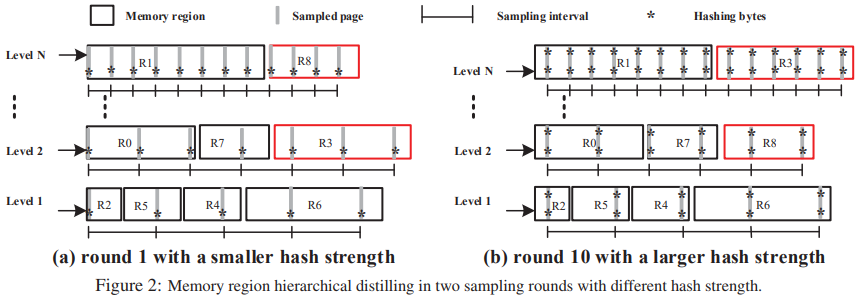 The higher the level is, the higher the page scanning frequency is.
The higher the level is, the higher the page scanning frequency is.
- Key characteristics for duplication qualities for each memory region
duplication ratio, average page lifetime, copy-on-write ratio those parameters can be collected from each round of sample
- UKSM can set threshold values for each of those parameters to decide whether this memory region can be promoted or demoted to other levels.
those thresholds are configurable, and can be set by the users depending on the targeted workload.
- Hierarchical sampling procedure Scan a level: For each region in different levels, it scans and samples the page according to the length of interval.
a higher level possesses a smaller interval
once a page is picked, it calculates the hash value of it according to current hash strength (bytes hashed in each page).
compare the hash value in two red-black trees and updates the counter of that region. (oen tree for management of merged page hashes, and one for management of unmerged page hashes)
After each global sampling round, the scanner estimates each region's duplication and COW-broken ratios.
Technology 2: Adaptive Partial Hashing
Goal: reduce per-page scan and deduplication cost (by partially hash a page).
Rational: the hash value is already sufficient to distinguish different pages, it does not need to hash a full page.
For its algorithm, it plans to finds the optimal strength for hte hash function (Global hashing strength)
profit: a weak hash strength can save more time penalty: a weak hash can increase the possibility of false positive, results in additional overhead of memcmp.
Implementation and Evaluation
- Implement in Linux and Xen
Around 6,000 lines of C code. Linux: UKSM hooks the linux kernel memory management subsystem for monitoring the creation and termination of application memory regions.
- Evaluation
- Memory Saving, CPU Consumption, Deduplication Speed Emulated workloads and real-word workloads, compare with the SuperFast Hash of the natvie Linux KSM scanner.
Emulated workload: emulate three kinds of workload: statically mixed workload, COW-broken workload, short-lived workload. Real-word workload: compare with XLH in ATC'13, Docker containers, desktop server.
- Analysis of Adaptive Partial Hashing
Scanning speed and deduplication speed on different degree redundant regions. the strength of hash function for different benchmark workloads
2. Strength (Contributions of the paper)
- This paper does a lots of experiments to prove different workloads can lead to different trade-off between memory saving and cpu consumption , as well as performance impact. This can make its motivation more strong.
3. Weakness (Limitations of the paper)
- In this paper, it does not investigate how to configure those parameters for different types of workload.
- For its part of partial hashing, I cannot understand the rationale behind it easily. And its adaptive partial hashing function is based on SuperFastHash, it can also consider other hash functions, and whether those types hash function can be adaptive.
4. Future Works
This paper targets memory deduplcation, which emphazies on responsiveness. How about back-up workload deduplication?
Can we try to classifiy different region, and for different region, we adopt different strategies to improve the performance. (Motivation?)